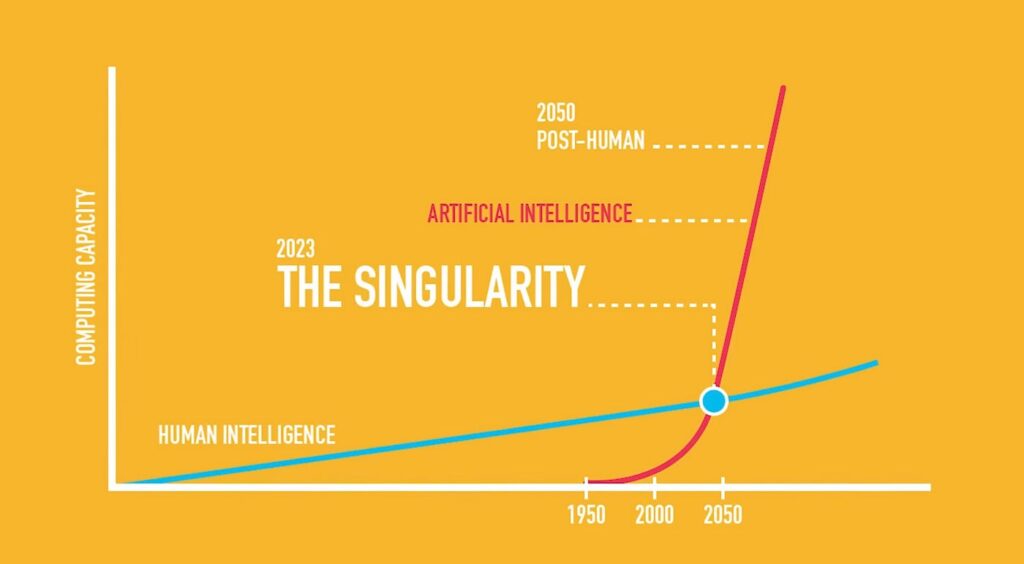
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has long been a topic of fascination and speculation, often accompanied by the concept of singularity. Singularity refers to a hypothetical point in the future where AI surpasses human intelligence, leading to rapid and unprecedented technological advancements. While the idea of singularity sparks both excitement and concern, it is essential to approach this concept with a clear understanding of its implications and the current state of AI. In this article, we will debunk common misconceptions about AI and singularity and explore the possibilities and challenges associated with these concepts.
Advertisement
Table of Contents
1. Understanding AI and Singularity
AI refers to the development of computer systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and problem-solving. Singularity, on the other hand, is a speculative concept representing a hypothetical future point where AI surpasses human intelligence, leading to profound and rapid changes in society.
2. Debunking Misconceptions
2.1 Singular Event
Singularity is often misconceived as a singular, abrupt event. However, it is more accurately viewed as a gradual process of advancing AI capabilities, rather than a specific moment in time.
2.2 Human-like Superintelligence
Contrary to popular belief, singularity does not necessarily imply the emergence of human-like superintelligence. AI can exhibit intelligence in specialized tasks without possessing the same breadth of capabilities as the human mind.
2.3 Fixed Timeline
The timeline for singularity remains uncertain and speculative. It is challenging to predict precisely when or if singularity will occur, as it depends on various technological, scientific, and societal factors.
2.4 Autonomous Agenda
Singularity does not imply an autonomous or self-directed agenda of AI. AI systems are created and governed by human developers, and their actions are guided by predefined algorithms and objectives.
2.5 Lack of Control or Ethical Considerations
The notion that singularity implies a lack of control or ethical considerations is unfounded. The responsible development of AI involves addressing ethical challenges, ensuring transparency, and incorporating human oversight to mitigate risks.
Additional Read: Safeguarding Data Privacy in AI: Ensuring Ethical and Secure Practices
Advertisement
3. The Current State of AI
To gain a clearer perspective, it is important to understand the current state of AI:
3.1 Narrow AI
The current state of AI primarily involves narrow or specialized AI systems designed to perform specific tasks, such as image recognition, natural language processing, or autonomous driving. These systems excel in their respective domains but lack the versatility of human intelligence.
3.2 General AI
General AI, or human-level AI, refers to AI systems capable of understanding, learning, and performing tasks across multiple domains, approaching the level of human intelligence. However, achieving this level of AI remains a significant scientific and technological challenge.
3.3 Artificial Superintelligence
Artificial superintelligence surpasses human intelligence in virtually every aspect. While the potential of artificial superintelligence is often associated with singularity, it remains speculative and lies beyond the current capabilities of AI.
3.4 Impact of AI in Various Fields
AI is already making significant impacts in various fields, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and entertainment. It enhances productivity, automates repetitive tasks, assists in decision-making, and offers new possibilities for innovation and problem-solving.
3.5 Ethical and Responsible AI Development
The ethical and responsible development of AI is crucial. As AI systems become more capable, ethical considerations such as fairness, transparency, accountability, and privacy need to be addressed to ensure AI benefits society while minimizing potential risks.
Additional Read: Addressing Job Displacement by AI: Navigating the Future of Work
Advertisement
4. Possibilities and Challenges
While the future implications of AI and singularity are uncertain, we can explore potential possibilities and challenges:
4.1 Positive Transformations
AI has the potential to bring about positive transformations in areas such as healthcare, education, environmental sustainability, and scientific research. It can augment human capabilities, improve efficiency, and address complex societal challenges.
4.2 Economic and Social Implications
The widespread adoption of AI may lead to significant economic and social transformations. It can result in job displacement, require new skill sets, and necessitate reimagining social structures and policies to ensure equitable access and benefits for all.
4.3 Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
As AI advances, ethical and regulatory frameworks must evolve to address concerns such as data privacy, bias, accountability, and the impact on human rights. Responsible AI governance is crucial to ensure the technology is deployed in a fair and transparent manner.
4.4 Human-Machine Collaboration
Rather than viewing AI as a replacement for humans, emphasis can be placed on human-machine collaboration. Combining human creativity, intuition, and empathy with AI’s computational power can lead to synergistic outcomes and novel solutions.
4.5 Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Continuous learning and adaptation are key to navigating the possibilities and challenges of AI. Ongoing research, interdisciplinary collaboration, and a commitment to addressing societal concerns will facilitate the responsible advancement of AI technologies.
5. Conclusion
AI and singularity are complex and multifaceted concepts that require a nuanced understanding. While singularity remains speculative, AI has already made significant advancements and is poised to bring about transformative changes. By debunking misconceptions, fostering responsible AI development, and addressing the possibilities and challenges, we can navigate the path forward and shape the future of AI in a way that aligns with human values and societal well-being.
Advertisement
6. FAQs
Q1: What is singularity in AI?
Singularity refers to a hypothetical future point where AI surpasses human intelligence, leading to rapid and unprecedented technological advancements.
Q2: Is singularity a singular event?
Singularity is not a singular event but rather a gradual process of advancing AI capabilities.
Q3: Can AI achieve human-like superintelligence?
While AI can exhibit intelligence in specialized tasks, achieving human-like superintelligence remains a significant scientific and technological challenge.
Q4: What are the current states of AI?
The current states of AI include narrow AI, general AI, and artificial superintelligence, with narrow AI being the most prevalent.
Q5: What are the possibilities and challenges of AI?
AI offers possibilities such as positive transformations, economic and social implications, ethical considerations, human-machine collaboration, and continuous learning. Challenges include ethical and regulatory considerations, societal impact, and the need for human adaptation and reskilling.